Subacromial Impingement classifications
- Stages of subacromial impingement: Neer’s classification
- Stages of subacromial impingement in athletes: Jobe’s classification
- Grading of impingement changes: Milgrom’s ultrasound classification
- Impingement lesions: Copeland Levy classification
Stages of subacromial impingement: Neer’s classification
Historical interest, stages do not necessarily follow one another
Stage 1: oedema and haemorrhage , age <25, reversible
Stage 2: fibrosis and tendinitis, age 25-40, recurrent pain with activity
Stage 3: bone spurs and tendon rupture, age >40, progressive disability
Stages of subacromial impingement in athletes: Jobe’s classification (1989)
1. Pure impingement with no instability
2. Primary instability with capsular and labral injury with secondary impingement which can be internal impingement or subacromial
3. Primary instability because of generalised ligamentous laxity with secondary impingement
4. Pure instability and no impingement
Grading of impingement changes: Milgrom’s ultrasound classification
Stage 1 - Bursal thickness 1.5 to 2.0mm
Stage 2 - Bursal thickness over 2.0mm
Stage 3 - Partial or full thickness tear of the rotator cuff
Impingement lesions: Copeland Levy classification
for more detail click here
Acromial Side |
Bursal Side |
|
|
|
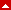 Top
Top

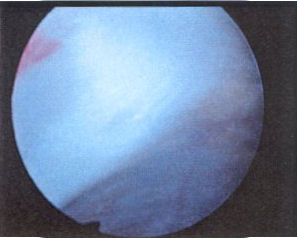 A0
A0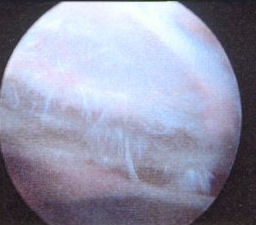 A1
A1 A2
A2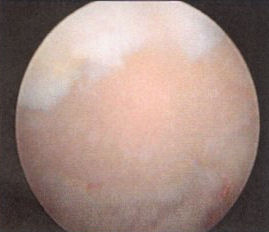 A3
A3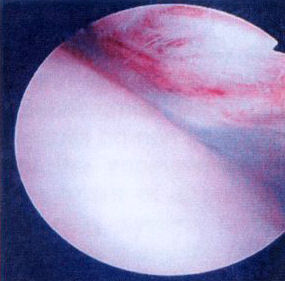 B0
B0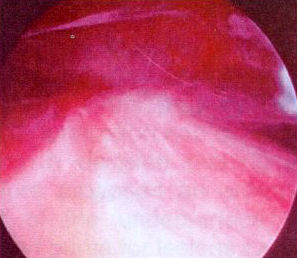 B1
B1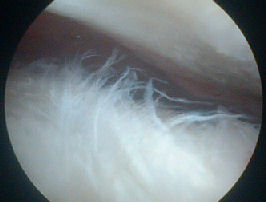 B2
B2 B3
B3 B4
B4