Scapula Fracture Classifications
- Scapula fractures: Euler and Rüedi classification
- Scapula fractures: DeCloux and Lemerle classification
- Scapula fractures: OTA Classification
- Glenoid fractures: Ideberg classification
- Glenoid fractures: Mayo classification
- Glenoid cavity fractures: Goss classsification
- Traumatic shoulder girdle / shoulder suspensory complex disruption : Goss
Scapular fractures: Euler and Rüedi classification
In: Schulterchirurgie.Edited by Habermeyer P, 261-272 ,1996
fractures of the body of scapula
isolated or multifragmentary
B. fractures of the process
B1 spine
B2 coracoid
B3 acromion
fractures of scapular neck
C1 anatomical neck
C2 surgical neck
C3 surgical neck with
a. fracture clavicle and acromion
b. torn CC and CA ligaments
D. Articular fractures
D1 glenoid rim
D2 glenoid fossa with
a. inferior glenoid fragment
b. horizontal split of scapula
c. coracoglenoid block formation
d. comminuted fractures
D3 scapula neck and body fracture
E. fracture combination
with humeral head fractures
 Top
Top
Scapular fractures: DeCloux and Lemerle classification
DeCloux MP, Lemerle, Omoplate. Lille Chir: 215-227, 1956
Type 1: Scapula body fractures
Type 2: Apophyseal fractures ( coracoid, acromion)
Type 3: fractures through the supero-lateral angle of scapula
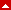
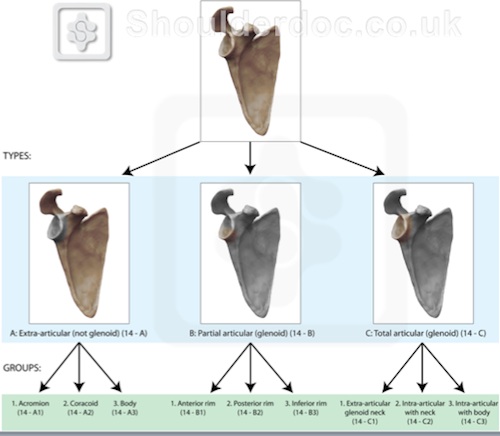
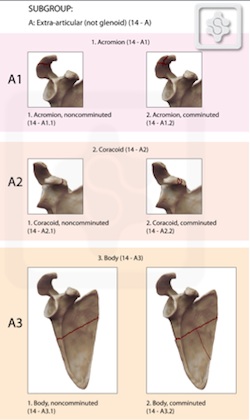
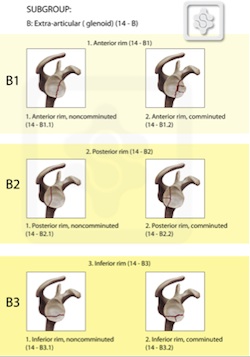
OTA Scapula fracture Classification System
Orthopedic Trauma Association
 Top
TopGlenoid fractures: Ideberg Classification
Ideberg R et al, Acta Orthop Scand, 66:395-397,1995
Based on 100 glenoid fractures reviewed over a 10-year period, and its merit lies largely in the epidemiologic con- text in which it was written.
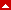
Type I: Avulsion fracture of the anterior margin.
Type II
Type IIA: Transverse fracture through the glenoid fossa exiting inferiorly.
Type IIB: Oblique fracture through the glenoid fossa exiting inferiorly.
Type III: Oblique fracture through the glenoid exiting superiorly; often associated with an acromioclavicular joint injury.
Type IV: Transverse fracture exiting through the medial border of the scapula.
Type V: Combination of a Type II and Type IV pattern.
Type VI: Severe continuation of glenoid surface (GOSS).
Ideberg R. fractures of the scapula involving the glenoid fossa. (From Batemans JE, Welsh RP (eds): In The surgery of the shoulder. Philadelphia, Decker 1984:63–66.)
Glenoid fractures: Mayo classification
Mayo modification of the Ideberg classification
Mayo KA, Benirschke SK, Mast JW: Displaced fractures of the glenoid fossa: Results of open reduction and internal fixation. CORR 347:122–130, 1998
Modification of the Ideberg classification based on 27 fractures treated surgically, as a more practical guide to fixation.
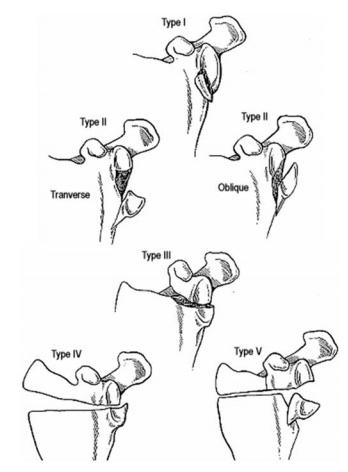
Type 1: anterior glenoid rim fracture
1A: fracture fragment 5mm or less
1B: fracture fragment > 5mm
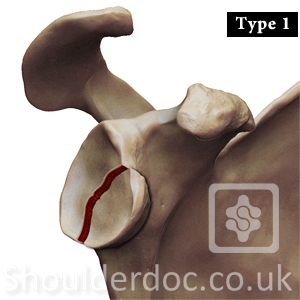
Type 2: inferior glenoid fracture involving part of the neck
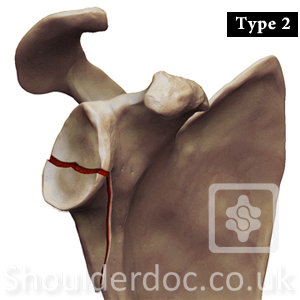
Type 3: superior glenoid fracture extending through
base of coracoid
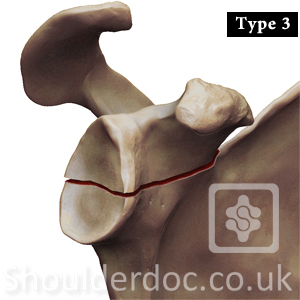
Type 4: Horizontal fracture involving scapular neck and body
fracture runs below the spine of scapula
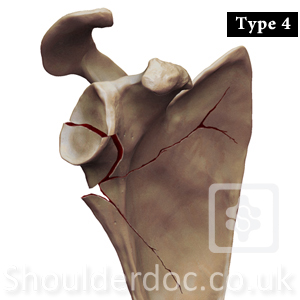
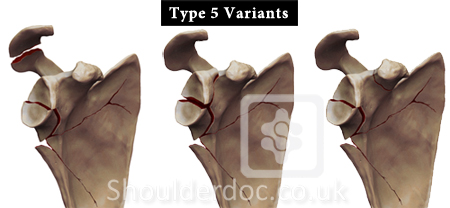
Type 5: Type 4 fracture with complete or incomplete
neck fracture
 Top
Top
Glenoid cavity fractures: Goss classsification
Goss TP, J Am Acad Orthop Surg, 3:22-33, 1995
A variation on Ideberg classification, with more subdivisions for improved discussion of operative management of these injuries.
Type 1: Glenoid rim fractures
A- anterior rim
B- Posterior rim
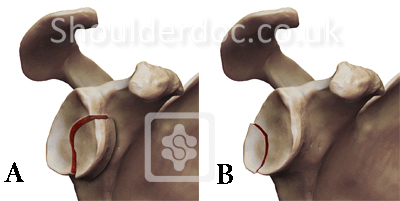
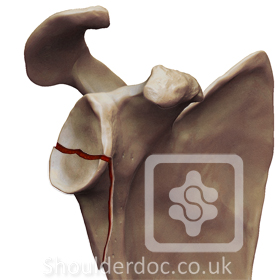
Type 2: Glenoid fracture exits at lateral border of scapula
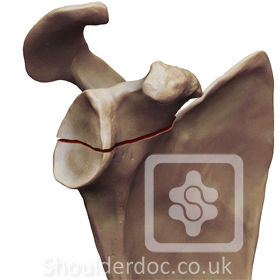
Type 3: Glenoid fracture exits at superior border of scapula
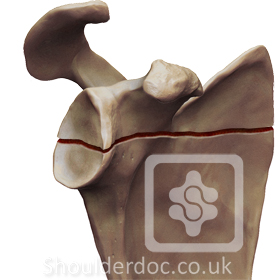
Type 4: Glenoid fracture exits at medial border of scapula
Type 5: Combination fractures
A- Types 2 & 4
B- Types 3 & 4
C- Types 2,3 & 4
D- comminuted
Types of traumatic shoulder girdle / shoulder suspensory complex disruption : Goss
Goss TP, J Am Acad Orthop Surg, 3:22-33, 1995
Single disruptions
Type A: single disruption by a break
Type B: single disruption by ligament disruption
Double disruptions
Type C: double ligament disruption
Type D: double break
Type E: combined bone and ligament disruption
Type F: both struts disrupted
Type G: one strut and one ring disruption


